wellhealthorganic.com:red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects

For centuries, spices have been utilized to enhance the taste and aroma of food while also potentially offering health advantages. One highly popular and widely used spice is the red chilli pepper. These small yet mighty peppers have been a staple ingredient in cuisines across the globe, adding a kick of flavour and potential health benefits. In this article, we will examine a detailed study that explores the various uses, advantages, and possible side effects of red chilli peppers. By reading this, you will gain valuable insights to help you make informed decisions about incorporating them into your diet. To learn more, continue reading the article on wellhealthorganic.com:red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects.
1. Uses in Cooking

Red chilli peppers are a flexible and tasty ingredient that finds their way into various dishes worldwide. They can be consumed fresh, dried, powdered, or incorporated into sauces, allowing individuals to adjust the spiciness and flavour. Let’s explore some common ways red chilli peppers are used in cooking:
Curry: Red chilli peppers are vital in numerous curry recipes from Indian, Thai, and Caribbean cuisines. They contribute both spiciness and vibrant colour to the dish. In Indian cooking, red chilli powder is commonly utilized, whereas Thai cuisine often uses fresh or dried red chillies.
Salsa: In Mexican and Tex-Mex cooking, red chilli peppers are employed in diverse salsas, offering a range of mild to intensely hot options. They can be combined with tomatoes, onions, cilantro, and other ingredients to create a flavorful accompaniment for tacos, tortilla chips, and various other dishes.
Hot Sauce: Red chilli peppers are the main component in numerous hot sauces. They can undergo fermentation and cooking or be used raw. They are frequently combined with vinegar, garlic, and other spices to produce a zesty and fiery condiment.
Kimchi: In Korean gastronomy, red chilli peppers prepare the renowned fermented side dish known as kimchi. Chilli pepper flakes, known as gochugaru, are mixed with Napa cabbage, garlic, ginger, and other ingredients, resulting in a piquant, tangy, and savoury condiment.
Chilli con Carne: Red chilli peppers play a crucial role in chilli con carne, a well-liked Tex-Mex dish featuring ground beef, beans, tomatoes, and spices. These peppers contribute both heat and depth to the flavorful concoction.
Soups and Stews: Red chilli peppers can be incorporated into various soups and stews to infuse them with spice and taste. They are frequently utilized in dishes like Mexican pozole, Thai tom yum, and Indian rasam, enhancing the flavours and adding a delightful kick.
Stir-fries and Noodle Dishes: Red chilli peppers are excellent for introducing heat and flavour to stir-fries and noodle dishes from various Asian cuisines. They are commonly employed in dishes like Chinese Kung Pao chicken, drunken Thai noodles (pad kee mao), and Indonesian mie goreng, lending a fiery and savoury element to the preparations.
Dry Rubs and Marinades: Red chilli pepper powder or flakes can be employed in dry rubs and marinades to introduce a fiery kick to grilled or roasted meats, poultry, and seafood, enhancing their taste and adding a delightful spiciness.
Pickling and Preserving: Red chilli peppers can be pickled or incorporated into preserves, contributing a spicy element to the preserved fruits or vegetables and providing a unique flavour profile.
Garnishing: Fresh or dried red chilli peppers can be used as a vibrant and zesty garnish on various dishes, lending flavour and visual appeal to the presentation.
These are merely a few examples that showcase the diverse culinary possibilities of red chilli peppers. With their ability to infuse heat, flavour, and colour, these versatile peppers can elevate a wide range of dishes, allowing for endless creativity in the culinary world.
2. Medicinal Applications

Numerous scientific investigations have delved into the potential medicinal benefits of red chilli peppers, with a particular emphasis on the active compound known as capsaicin. Various journal publications have highlighted evidence-based medicinal uses of red chilli peppers, including the following:
Pain Alleviation: Capsaicin possesses pain-relieving properties, making it effective in mitigating pain caused by conditions like arthritis, neuropathy, and muscle pain. Over-the-counter topical creams and capsaicin patches are available to provide relief (Source: Journal of Pain Research, 2016).
Treatment for Psoriasis: Capsaicin-based creams have shown effectiveness in reducing the scaling, redness, and itching associated with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition (Source: Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 1993).
Support for Weight Management: Capsaicin exhibits thermogenic properties, which means it can enhance energy expenditure and fat oxidation. Some studies suggest that consuming capsaicin may aid in weight loss and prevent weight gain by boosting metabolism (Source: Appetite, 2012).
Cancer Prevention: Certain studies indicate that capsaicin may possess properties that can inhibit specific cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis (cell death) in others, suggesting its potential as an anti-cancer agent (Source: Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 2016).
Gastrointestinal Well-being: Capsaicin has demonstrated gastroprotective effects, which can help reduce the risk of gastric ulcers and enhance digestion by stimulating gastric acid secretion and promoting gut motility (Source: Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2006).
Heart Health: Preliminary research suggests that capsaicin might contribute to cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure, enhancing blood vessel function, and potentially reducing the likelihood of atherosclerosis (Source: Progress in Drug Research, 2014).
Although there is potential for the medicinal applications of red chilli peppers, it is important to acknowledge that much of the research conducted is still in the early stages. Extensive clinical trials are necessary to validate these findings more conclusively. It is advisable to seek advice from a healthcare professional before using red chilli peppers or capsaicin-based products for medicinal reasons, particularly if you have existing medical conditions or are taking medications.
Benefits of Red Chili Peppers

Benefits of Red Chili Peppers
1. Anti-inflammatory Properties
Reducing Inflammation: Red chilli peppers, specifically capsaicin, have shown anti-inflammatory properties that can positively affect various health conditions. The main reason behind these properties is capsaicin’s ability to suppress the production of inflammatory substances in the body. Here are some advantages of the anti-inflammatory properties of red chilli peppers:
Alleviating Arthritis: Capsaicin has been discovered to relieve joint pain and inflammation commonly experienced in arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Topical creams containing capsaicin can be applied to the affected area, reducing the production of substance P, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain (Source: Clinical Rheumatology, 2010).
Reducing Muscle Pain and Soreness: The anti-inflammatory properties of capsaicin can help decrease muscle pain and soreness caused by exercise or injury. Applying topical creams or capsaicin patches to the affected muscles can temporarily relieve inflammation (Source: Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2011).
Easing Migraines and Headaches: Capsaicin has shown significant effectiveness in diminishing the occurrence and severity of cluster headaches and migraines. The application of capsaicin directly to the nasal passages can provide relief from pain by desensitizing the trigeminal nerve, responsible for transmitting pain signals during these types of headaches(Source: Headache, 1993).
Respiratory Symptom Relief: The anti-inflammatory properties of capsaicin can clear symptoms associated with respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Studies have shown capsaicin can reduce airway inflammation, improving respiratory function (Source: Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2017).
Reduction of Skin Inflammation: Capsaicin has demonstrated its ability to reduce inflammation in conditions like psoriasis and dermatitis. Topical creams containing capsaicin can provide relief from itching, redness, and scaling by inhibiting the production of inflammatory substances in the skin (Source: Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 1993).
The anti-inflammatory properties found in red chilli peppers offer potential as a natural remedy for a range of health conditions characterized by inflammation. However, seeking advice from a healthcare professional before incorporating capsaicin or red chilli peppers into a medicinal regimen is crucial, as individual reactions can vary, and specific individuals may experience adverse effects.
2. Boosting Metabolism
The active compound capsaicin found in red chilli peppers has been demonstrated to increase the metabolic rate, leading to more efficient calorie burning. This thermogenic effect can be beneficial for individuals seeking to manage their weight and promote a healthy metabolism. Here are some advantages of red chilli peppers as a metabolism booster:
Increased Thermogenesis: Capsaicin stimulates thermogenesis, contributing to the body’s calorie-burning capacity. Raising the body’s core temperature promotes energy expenditure, assisting individuals in managing their weight effectively (Source: International Journal of Obesity, 2012).
Enhanced Fat Oxidation: Research suggests capsaicin promotes the breakdown of stored fat for energy, a process known as fat oxidation. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals aiming to lose weight, as capsaicin supplementation has been found to increase fat oxidation during physical activity, potentially improving exercise performance (Source: Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 2007).
Appetite Suppression: Capsaicin has been associated with appetite suppression, which can contribute to calorie reduction and weight loss. By influencing the release of hormones like ghrelin, which regulate hunger, capsaicin may help individuals better control their food intake (Source: Physiology & Behavior, 2011).
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: Animal studies have indicated that capsaicin has the potential to improve insulin sensitivity, a crucial factor in preventing weight gain and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. By improving insulin sensitivity, capsaicin facilitates more efficient uptake of glucose by the body’s cells, thereby reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (Source: Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2013).
Synergistic Effects with Complementary Bioactive Compounds: Some research suggests that combining capsaicin with other bioactive compounds, such as green tea extract, may synergistically affect metabolism and weight loss. These combinations could amplify the benefits associated with metabolic processes (Source: Clinical Nutrition, 2009).
The ability of red chilli peppers to enhance metabolism and support weight management can be a valuable asset for individuals seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle and balanced diet. However, it’s important to recognize that the impact of capsaicin on metabolism can differ among individuals.
Therefore, it is strongly advised to consult with a healthcare professional before considering capsaicin supplements or significantly increasing the consumption of red chilli peppers as part of a weight management strategy. Their expertise will ensure a safe and personalized approach to achieving your goals.
3. Improving Digestive Health
Red chilli peppers, specifically the active compound capsaicin, have been associated with enhanced gastrointestinal well-being. Capsaicin has the potential to positively influence digestion by stimulating the production of stomach acid, facilitating gut motility, and promoting overall digestive function. Below are some advantages of red chilli peppers in promoting digestive health:
Boosted Stomach Acid Production: The active compound capsaicin found in red chilli peppers has been discovered to stimulate the production of stomach acid, which plays a crucial role in effectively breaking down and digesting food. Sufficient stomach acid levels are essential in preventing indigestion and mitigating various gastrointestinal problems (Source: Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2006).
Improved Gut Motility: By activating the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channel in the gut, capsaicin can enhance gut motility, which refers to the movement of food through the digestive system. Enhanced gut motility aids in preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements (Source: Pflügers Archiv – European Journal of Physiology, 2004).
Reduced Risk of Gastrointestinal Issues: Consuming moderate amounts of red chilli peppers has been associated with a decreased risk of developing gastrointestinal problems, including peptic ulcers. The gastroprotective properties of capsaicin contribute to preserving the integrity of the stomach lining and inhibiting ulcer formation (Source: World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2016).
Antibacterial Properties: Red chilli peppers have been discovered to possess antibacterial properties, which can aid in inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria within the gut. Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is crucial for promoting overall digestive health and supporting immune function (Source: Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2006).
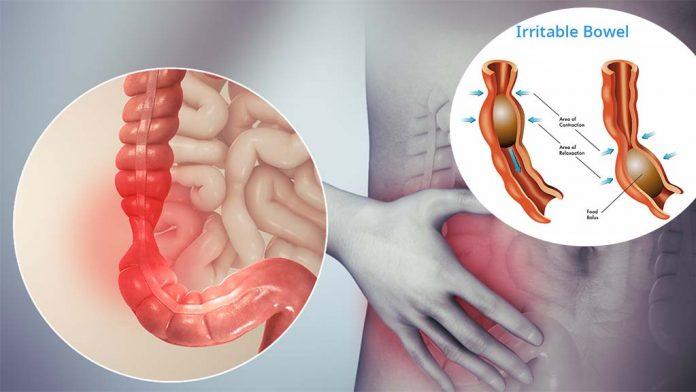
Alleviation of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Symptoms: Some studies have indicated that capsaicin may have the potential to alleviate symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome, such as abdominal pain and bloating. This is achieved by reducing inflammation and enhancing gut motility (Source: United European Gastroenterology Journal, 2014).
It is important to understand that people can have different reactions to capsaicin and red chili peppers, and some individuals may encounter gastrointestinal discomforts such as heartburn or diarrhea when consuming spicy foods. To mitigate these possible side effects while still enjoying the digestive health benefits of red chili peppers, it is recommended to gradually incorporate them into the diet and consume them in moderation.
4. Enhancing Circulation
Red chilli peppers, specifically capsaicin, have been shown to positively affect circulation, contributing to overall cardiovascular health. Capsaicin aids in enhancing blood flow and promoting the optimal functioning of blood vessels by stimulating the release of specific molecules and influencing blood pressure regulation. Here are some advantages of red chilli peppers in improving circulation:
Vasodilation: Capsaicin has been shown to induce the release of nitric oxide, which facilitates the relaxation of blood vessels, leading to vasodilation. This expansion of blood vessels can enhance blood flow and help lower blood pressure, thereby supporting cardiovascular well-being (Source: Hypertension, 2010).
Blood Pressure Regulation: Capsaicin acts on the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channel, a component involved in blood pressure regulation. By influencing this channel, red chilli peppers containing capsaicin can assist in reducing blood pressure levels, promoting healthy blood pressure, and decreasing the risk of hypertension (Source: Cell Metabolism, 2010).
Enhanced Function of Blood Vessels: Scientific research indicates that capsaicin can potentially improve the function of blood vessels by reducing inflammation and stimulating the release of substances that promote vasodilation. This improved function of blood vessels can contribute to the prevention of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing and hardening of arteries (Source: Atherosclerosis, 2013).
Improved Blood Circulation in Extremities: Through its ability to promote vasodilation and enhance blood vessel function, capsaicin has been found to facilitate better blood flow to the extremities, such as the hands and feet. This improved circulation can relieve cold feet and hands symptoms and enhance overall comfort (Source: The Journal of Physiological Sciences, 2017).
Potential Stimulation of Angiogenesis: Certain studies have suggested that capsaicin may stimulate angiogenesis, making new blood vessels from ones which already exist, under specific circumstances. Angiogenesis can be beneficial in enhancing blood circulation and supporting tissue repair following an injury (Source: Cancer Research, 2004).
The advantages of red chilli peppers in improving circulation can support cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that people may have different reactions to capsaicin and red chilli peppers. It is advisable to consume red chilli peppers in moderation and seek guidance from a healthcare professional before considering capsaicin supplements or significantly increasing the intake of red chilli peppers for circulation-related benefits.
5. Supporting Immune Function
Red chilli peppers, rich in vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds, have the potential to enhance immune function by fortifying the body’s innate defence mechanisms. The following are some advantages of red chilli peppers in supporting immune function:
Abundant in Vitamin C: Red chilli peppers possess a high content of vitamin C, an important nutrient that plays a vital role in bolstering immune system function. Vitamin C aids in the production and activity of white blood cells, which defend the body against infections and diseases. Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of vitamin C safeguard immune cells against harm caused by free radicals (Source: Nutrients, 2017).
Significant Source of Vitamin A: Red chilli peppers are a significant source of vitamin A, primarily in the form of beta-carotene. Vitamin A contributes to immune system support by preserving the skin’s and mucous membranes’ integrity, acting as the body’s initial barrier against pathogens. Additionally, vitamin A is crucial for properly functioning various immune cells, including natural killer cells and T-cells (Source: Journal of Clinical & Cellular Immunology, 2018).
Anti-inflammatory Properties: The presence of capsaicin, the active compound in red chilli peppers, grants them anti-inflammatory properties that assist in regulating the immune system’s response. By reducing inflammation, capsaicin can help prevent excessive immune reactions that could result in chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders (Source: Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2017).
Antioxidant Effects: Red chilli peppers contain a variety of antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, as well as carotenoids, which can counteract the effects of free radicals and mitigate oxidative stress. By safeguarding immune cells against damage and enhancing overall immune function, the antioxidants in chilli peppers contribute to a stronger immune system (Source: Food Chemistry, 2011).
Antimicrobial Activity: The antimicrobial properties of capsaicin and other active compounds found in red chili peppers have been observed to hinder the growth of specific bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This antimicrobial activity assists the immune system in fighting against infections(Source: Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2006).
Incorporating red chilli peppers into a well-rounded diet can enhance immune function and promote overall well-being. However, it is crucial to consume them in moderation, as excessive intake may cause gastrointestinal discomfort in specific individuals. As always, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating capsaicin supplements or making substantial dietary adjustments for immune support.
Side Effects of Red Chili Peppers
Although red chilli peppers provide a multitude of health advantages, they can also result in adverse effects, particularly when consumed excessively or by individuals with specific medical conditions.
1. Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Despite the various health benefits associated with red chilli peppers, some people may experience gastrointestinal discomfort as a potential side effect, especially when consuming excessive amounts or having a sensitive digestive system. Here are some possible adverse effects of red chilli peppers that can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort:
Heartburn: The active compound capsaicin found in chilli peppers can relax the lower oesophagal sphincter, letting stomach acid to flow back into the oesophagus. This can result in a burning sensation in the throat and chest known as acid reflux or heartburn (Source: Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2000).
Stomach Pain and Cramping: Certain individuals might encounter abdominal pain or cramps following the consumption of spicy foods containing capsaicin. This discomfort can be linked to the increase in gastric acid production or the activation of pain receptors in the stomach lining (Source: Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology, 2009).
Diarrhoea: Eating red chili peppers can trigger the release of specific hormones that enhance intestinal movement, which may result in diarrhea for certain individuals. Furthermore, the irritating properties of capsaicin on the digestive system can also contribute to the occurrence of diarrhea. (Source: Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2006).
Nausea and Vomiting: In some instances, the consumption of large quantities of capsaicin or red chilli peppers may lead to feelings of vomiting and nausea, mainly among people with sensitive stomachs or those spicy foods (Source: Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology, 2003).
Aggravation of Gastrointestinal Disorders: Individuals who already have gastrointestinal disorders like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may find that their symptoms worsen after consuming red chili peppers or foods containing capsaicin (Source: The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 1999).
2. Skin Irritation
Red chilli peppers, specifically capsaicin, have the potential to induce skin irritation in specific individuals, especially when the peppers make direct contact with the skin. Here are some possible adverse effects of red chilli peppers associated with skin irritation:
Contact Dermatitis: For certain individuals, coming into contact with red chili peppers or products containing capsaicin can lead to the development of contact dermatitis. This condition involves inflammation of the skin and is characterized by symptoms such as redness, itching, and swelling. It occurs when the skin reacts to an irritant or allergen (Source: Dermatitis, 2006).
Burning Sensation: Upon contact, capsaicin has the ability to stimulate pain receptors in the skin, resulting in a sensation of burning. The intensity of this burning sensation can vary depending on an individual’s sensitivity to capsaicin and the concentration of capsaicin present in the chili pepper (Source: British Journal of Anaesthesia, 2008).
Side Effects of Capsaicin Cream: When capsaicin creams are applied topically for pain relief in different conditions, they have the potential to cause skin irritation. This can manifest as redness, itching, burning, and stinging sensations. Generally, these side effects are mild and temporary, but in certain individuals, they may be more severe (Source: Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2000).
Chilli Burn: It is important to be careful when dealing with red chili peppers to prevent any contact with sensitive parts of the body such as the nose, eyes, and genitals. Capsaicin, the active compound in chili peppers, can cause considerable irritation and a sensation of burning in these areas, commonly known as chili burn (Source: Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2011).
Allergic Reactions: Although it is uncommon, there are cases where certain individuals may have allergic reactions to red chili peppers or capsaicin, resulting in symptoms like skin rashes, hives, and swelling. If you suspect an allergic reaction, it is crucial to promptly seek medical assistance (Source: Allergologia et Immunopathologia, 2016)
To avoid skin irritation from red chilli peppers, handling them carefully, using gloves if needed, and ensuring thorough hand washing after contact. If you encounter severe or long-lasting skin irritation following exposure to red chilli peppers, seeking guidance and personalized advice from a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options is recommended.
3. Allergic Reactions
While uncommon, specific individuals can have allergic reactions to red chilli peppers or capsaicin, their active component. Allergic responses to chilli peppers can vary in intensity, spanning from mild to severe, and it is essential to be mindful of the potential adverse effects:
Skin Irritation and Hives: Allergic reactions to red chili peppers can cause the appearance of skin rashes or hives, which are characterized by patches of red, itchy, and raised skin. These reactions can occur either upon direct contact with chili peppers or after consuming them (Source: Allergologia et Immunopathologia, 2016).
Swelling: In some cases, an allergic reaction to red chili peppers can result in swelling localized around the eyes, lips, or tongue. This swelling can be uncomfortable and, in severe instances, may obstruct the airway (Source: Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, 1999).
Respiratory Symptoms: Exposure to red chili peppers can induce respiratory symptoms in the form of sneezing, nasal congestion, a runny nose, wheezing, and respiratory difficulties as a result of allergic reactions. Those with asthma may experience a deterioration of their condition when exposed to chili peppers (Source: Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2001).
Gastrointestinal Issues: Certain individuals may experience gastrointestinal complications such as queasiness, throwing up, looseness of the bowels, and abdominal discomfort as a result of an allergic reaction to red chili peppers or capsaicin (Source: Allergologia et Immunopathologia, 2016).
Anaphylaxis: In extremely rare cases, individuals may experience a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis after exposure to red chili peppers or capsaicin. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, dizziness, and a sudden drop in blood pressure. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention (Source: Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology, 2014).
If you have concerns about being allergic to red chili peppers, it is crucial to refrain from further exposure and seek guidance from a healthcare professional regarding diagnosis and treatment. If you encounter any indications of anaphylaxis, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wellhealthorganic.com:red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects, Red chilli peppers are a versatile and tasty ingredient that can provide numerous health advantages, including inflammation reduction and assistance with weight management. Nevertheless, it is crucial to be cautious about potential adverse effects, mainly if you are sensitive to spicy foods or have existing health conditions. Now you have gained knowledge about various aspects of red chilli peppers, such as their uses, benefits, side effects, and more, from wellhealthorganic.com: “red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects”.
Read More: wellhealthorganic.com:red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects- wellhealthorganic.com:easy-way-to-gain-weight-know-how-raisins-can-help-in-weight-gain
- Wellhealthorganic.com:Facial-Fitness-Anti-Aging-Facial-Exercises-To-Look-Younger-Every-Day | Check It Out
- wellhealthorganic.com:5-amazing-health-benefits-of-guava
- wellhealthorganic.com:red-chilli-you-should-know-about-red-chilli-uses-benefits-side-effects
- How the Gut and Brain Work Together
- What is irritable bowel syndrome Causes and Treatment
- Self Hypnosis for Sleep: What it is & how to do it
- How Long Does Heroin Stay In Your Body?
- Detox Drinks For Weed Elimination From System
- 10 Different Types of Yogurt